Our way to detect magnons: Brillouin light scattering microscopy
Nanoscaled Magnonic Networks
Our view of the building blocks for magnetic components and their assembly on the chip.
Roadmap on spin-wave computing
Check out this comprehensive description of recent developments and trends in magnonic computing.
CoSpiN “Coherent Networks for Neuromorphic Computing” funded by the ERC
Spin waves, the elementary low energy excitations of an ordered spin system, and their bosonic quanta, magnons, carry energy and angular momentum in the form of spin. The field of magnonics aims to create devices for sensing, data processing and logic which are based on spin waves and their outstanding properties like intrinsic nonlinearity and nanometer wavelengths at GHz frequencies.
Our scientific aim is to explore and combine emerging physical phenomena which can be used to realise novel magnonic hybrid systems with novel and superior characteristics. We have a particular focus on:
- Nonlinear spin-wave phenomena in micro- and nanostructures
- Nanoscaled magnonic devices for unconventional data processing
- Novel materials for magnonics including low-damping Heuler compounds
- Hybrid systems combining magnonics with spintronic and phononic systems
- Amplification and control of coherent spin-waves in micro-and nanostructures using parametric processes
- Nonreciprocal magnonic systems based on dipole-dipole and DMI interactions
To achieve our goals, we investigate magnonics systems experimentally by Brillouin light scattering spectroscopy and inductive techniques. To study and optimize magnonic systems before fabrication, we employ massively parallelized micromagnetic simulations. These simulations are run and analysed by our home-made AITHERICON software platform with the aim to use artificial intelligence, neural networks and inverse design methods to create magnonic systems with designed and superior properties for wave-based transport and data processing.
News
SELECTED RECENT PUBLICATIONS AND ACCEPTED SUBMISSIONS
Link to FULL PUBLICATION LIST
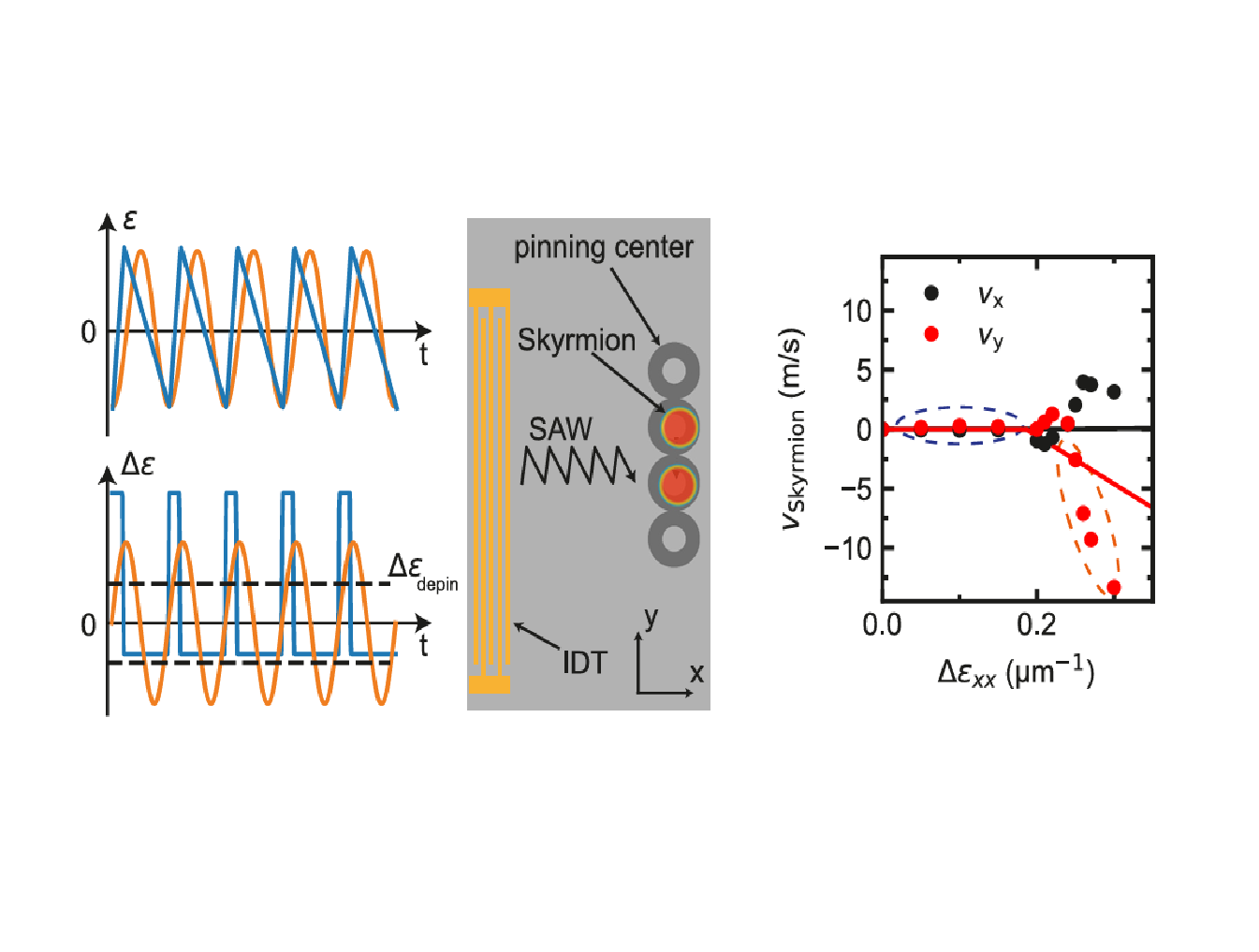
- Ratchet motion of magnetic skyrmions driven by surface acoustic sawtooth wavesPhilipp Schwenke*, Ephraim Spindler, Vitaliy I. Vasyuchka, Alexandre Abbass Hamadeh, Philipp Pirro, and Mathias Weiler Phys. Rev. B 112, 214409 (2025)arXiv.2503.09506
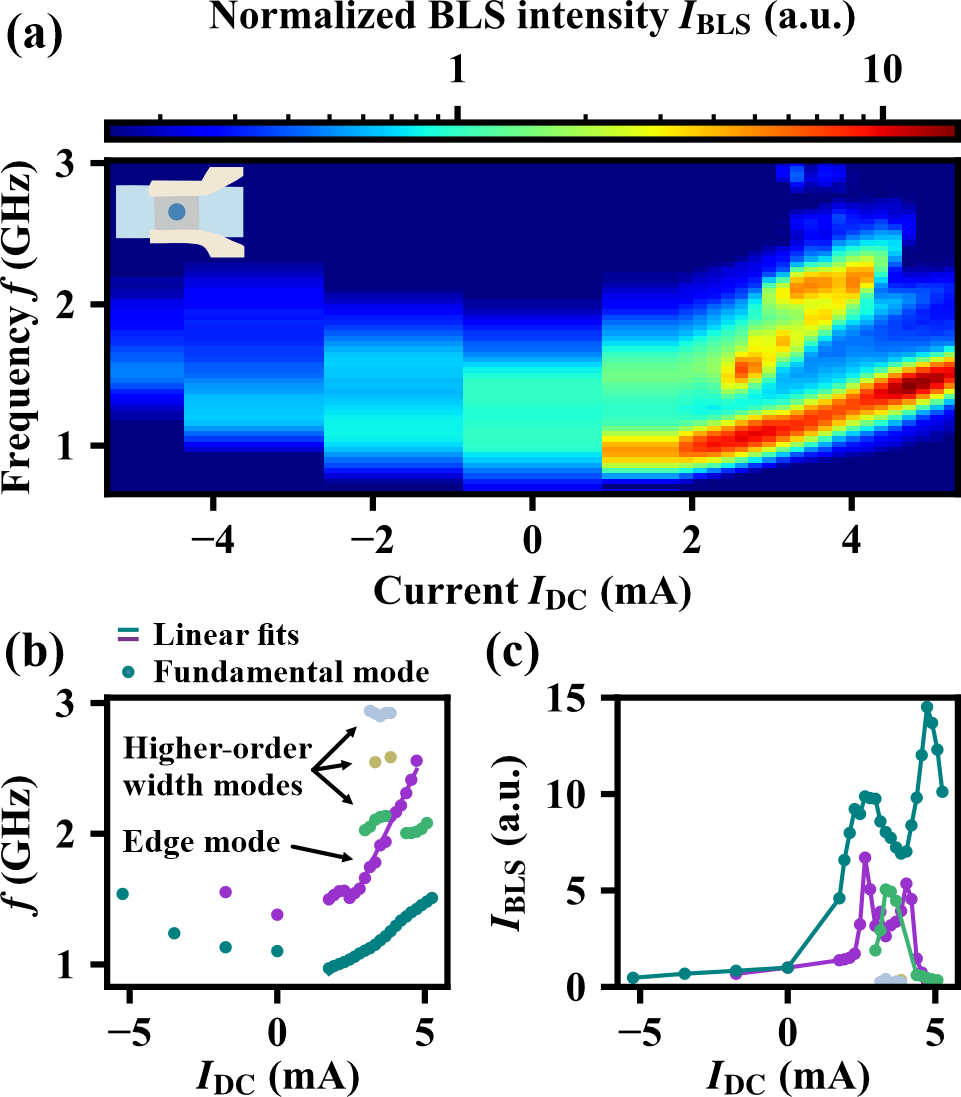
- Spin-wave emission with current-controlled frequency by a PMA-based spin-Hall oscillatorMoritz Bechberger, David Breitbach, Abbas Koujok, Björn Heinz, Carsten Dubs, Abbass Hamadeh, Philipp Pirro2512.00593
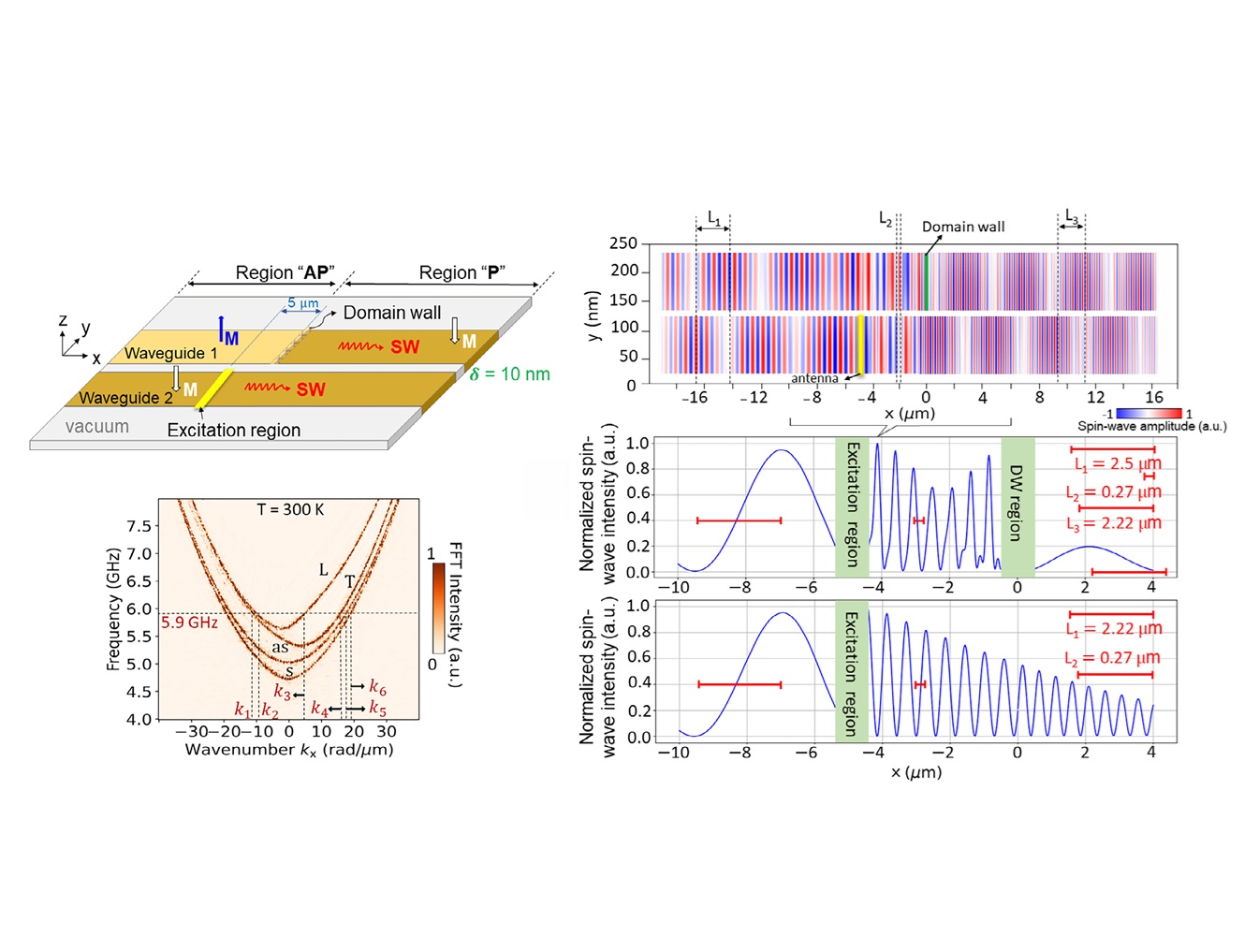
- Nonreciprocal Spin Waves in Out-of-Plane Magnetized Coupled Waveguides Reconfigured by Domain Wall DisplacementsHanadi Mortada, Roman Verba, Qi Wang, Philipp Pirro, Alexandre Abbass Hamadehadvanced electronic materials e00575, (2025)
- Magnon-polaron control in a surface magnetoacoustic wave resonatorKevin Künstle, Yannik Kunz, Tarek Moussa, Katharina Lasinger, Kei Yamamoto, Philipp Pirro, John F Gregg, Akashdeep Kamra, Mathias WeilerNature Communications 16, 10116 (2025)arXiv.2506.09717
- Three-dimensional nanoscale control of magnetism in crystalline Yttrium Iron GarnetV. Levati, M. Vitali, A. D. Giacco, N. Pellizzi, R. Silvani, L. C. Mavilla, M. Madami, I. Biancardi, D. Girardi, M. Panzeri, P. Florio, D. Breitbach, P. Pirro, L. Rovatti, N. Lecis, F. Maspero, R. Bertacco, G. Corrielli, R. Osellame, V. Russo, A. L. Bassi, S. Tacchi, D. Petti, E. AlbisettiNature Communications 16, 9602 (2025)arXiv.2409.17722